Introduction
Texas has experienced a substantial demographic transformation from aging predominantly white population to people of color previously considered as minorities. Over 26% of the current population in Texas are under the age of 18 yrs. According to the United States Census Bureau, out of a projected population of over 28.3 million in July 2017, 39.4% are of Hispanic or Latino origin. This number has increased as shown in Table 1 below. As Steven Klineberg, a professor at Rice University put it, there won't be a force high enough to stop the transformation of Texas into a majority of people of color. According to the professor, the only way to deal with the situation is through empowerment of young children the majority of which are poor through educational opportunities. This will enable them to have successful competitions in the global information arena.
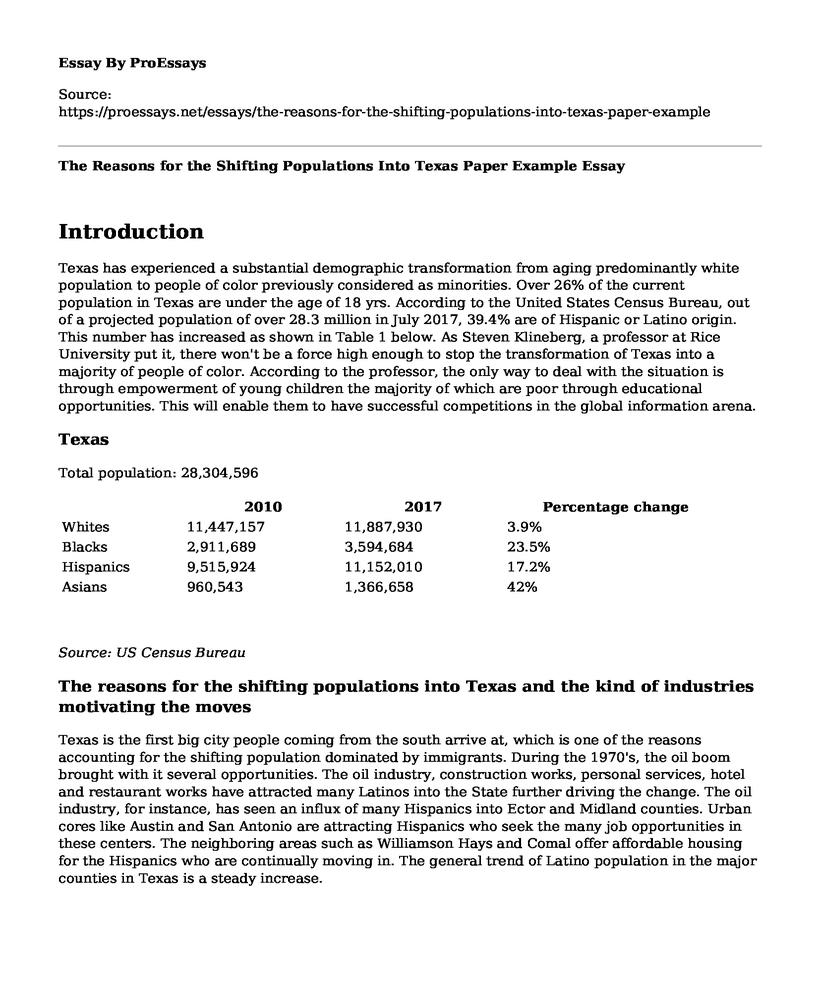
Texas
Total population: 28,304,596
| 2010 | 2017 | Percentage change | |
| Whites | 11,447,157 | 11,887,930 | 3.9% |
| Blacks | 2,911,689 | 3,594,684 | 23.5% |
| Hispanics | 9,515,924 | 11,152,010 | 17.2% |
| Asians | 960,543 | 1,366,658 | 42% |
Source: US Census Bureau
The reasons for the shifting populations into Texas and the kind of industries motivating the moves
Texas is the first big city people coming from the south arrive at, which is one of the reasons accounting for the shifting population dominated by immigrants. During the 1970's, the oil boom brought with it several opportunities. The oil industry, construction works, personal services, hotel and restaurant works have attracted many Latinos into the State further driving the change. The oil industry, for instance, has seen an influx of many Hispanics into Ector and Midland counties. Urban cores like Austin and San Antonio are attracting Hispanics who seek the many job opportunities in these centers. The neighboring areas such as Williamson Hays and Comal offer affordable housing for the Hispanics who are continually moving in. The general trend of Latino population in the major counties in Texas is a steady increase.
Issues that would motivate minorities and the youth voting population (18+) to participate in voting
Voting accords the people the power to be involved in decision making about issues that affect them in their daily lives. The ability to make decisions empowers minorities who are less economically privileged to bridge the gap of inequality and isolation. Structural socioeconomic inequality often produces political inequality and relative exclusion from important political discussions (Ranciere, 2006). Thus poor and working-class people often do not have their interests and prospects as well represented as those of the middle and upper classes. In many political systems, minorities occupy small proportions of public charters elected, as well as being relatively fewer in powerful and influential positions in the general public life. Minority cultural groups and those in devalued racial positions also often lack an effective political voice. Many consider this exclusion or political marginalization of subordinate groups and individuals to be incorrect, as this frustrates the promises of political equality and opportunity that underlie democratic principles.
Greater political inclusion and influence to underrepresented social groups can contribute to a society facing and reducing structural social inequality (Ranciere, 2006). Political equality commitment implies that democracy must encompass minority groups which are likely to be excluded from the discussions in the absence of such measures. These groups constitute a relatively small minority or are socially or economically disadvantaged, or else other perspectives dominate the prevailing political discourse. As argued by Duflo (2005), minority groups should be recognized and included in their specificity in democratic communicative processes. An essential way of promoting greater inclusion of members of underrepresented social groups is through political arrangements specifically designed to increase representation of women, racial or ethnic minorities, disadvantaged castes, and so on. Thus, schemes such as quotas on party lists, proportional representation, reserved parliamentary seats and delimitation of special electoral districts, among others should be implemented to motivate the youth and minorities to participate in elections thus promoting democratic representation.
Issues keeping youth and minorities from the polls
By their social positioning, members of structurally differentiated groups often have different understandings about the causes of problems and conflicts and the possible effects of proposed solutions. Each group has different perceptions about the others, and different understandings about the history and the current configuration of social relations. Political representation by self-government is justified by combating systematic discrimination in both the political system and the society generally (Barrett & Brunton-Smith, 2014).
Whether young people and minorities would be more likely to participate in politics if they are being represented by someone who looks more like them
The process of mobilizing members of a group for inclusion and participation in representative institutions and discussions of issues on the agenda of society frequently rightly invokes self-images of distinction and pride. As Duflo (2005) posited, this justifies the representation of groups regarding diversity and recognition or affirmation of group identity. Many doubt that the specific representation of minorities promotes justice or is pertinent. Some argue that individuals should rely directly on political institutions without group meditation and that aggregating individual votes in constituencies to elect representatives is the only way to implement such political individualism. Others, as I have already pointed out, considered the representation of groups suspected of a biased and misguided essentialisation.
Several theorists object to what is called "descriptive" representation or "mirror" representation (Barrett et al., 2014). The conception of this image of representation asserts that a representative organism must seem like a copy of the social organism to which it belongs so that it must contain members of the distinct social groups in proportion as they are found in society in general. Pitkin argues that such a conception regards the act of representing simply as a way of 'replacing' or 'putting in,' rather than thinking of it as an activity (Howarth, Andreouli & Kessi, 2014). However, many who advocate the specific representation of minorities would find absurd the suggestion that physical attributes or belonging in themselves could support the representation of certain people with similar qualities. Instead, they argue, minorities have identical experiences that only members of their groups can understand with the same immediacy. For others, however, justifying the representation of groups in terms of experiences, interests, or opinions supposedly shared by all members of the group obscures their internal differences and erroneously reduces all members to a common essence, so that groups would become so distinct from one another that it would be impossible for them to understand and cooperate in their differences.
How the minority/youth vote might impact Texas politics and whether a "Hispanic Texas" automatically means a blue one
As stated previously, over a quarter of the State's population constitutes of young adults most of whom are people of color. These adults have in the past not participated in political processes as reflected in the low voter turnout of less than 50% in the last election. Vibrant youths are leading several social movements in the state. If this energy were to continue, and with voter education, more young people will be motivated and will participate in voting which is likely to shift the politics of Texas from former Republican to democrat orientation.
How the shift in Texas might impact the United States on the whole
The Texas population has increased by 12.6% from 25.1 million in the 2010 census to the current 28.7 million according to the world population review. It is estimated that by 2022, the Latino population will exceed the Texas whites. The United States is gradually becoming a nation of immigrants meaning that the political spectrum is shifting towards a more political representation of these once minority populations. The inevitable demise of Anglos popularity necessitates the debates on how to modify policies and proposals about equality and political inclusion.
Few advocates of a model of deliberative or communicative democracy would claim that it applies primarily to situations where people are mutually present in the same space and for a given occasion to confront and speak directly. However, both in theory and in practice there is a tendency to associate democratic communicative processes with face-to-face interactions. Whether they assume that the democratic discussion takes place in a parliamentary session or a meeting of a group of citizens, these supporters generally end up representing the process of democratic communication as centered in some space where participants are mutually present.
A stable democracy indeed requires many occasions when public authorities and citizens discuss individual experiences and issues. However, to theorize democracy as a communication process aimed at reaching decisions does not adequately correspond to the need to conceptualize the decentralized democracy of large mass societies. In a complex society with many millions of people, democratic communication consists of fluid, overlapping and divergent discussions and decisions, dispersed both in space and time. In the context of these societies, there are widespread complaints that point out the exclusionary character of the norms of representation (Howarth et al., 2014).
People often complain that social groups of which they are part or with which they have affinity are not represented adequately in influential forums of government such as legislatures, commissions, and councils, as well as in the individual coverage of the media. Greater political inclusion in democratic processes advocate measures that provide greater representation of underrepresented groups, especially when these groups are minorities or are subject to structural inequalities. From the movements of women from many quarters of the world, for example, they point out that legislatures occupied mainly by men cannot aggressively represent women. In response to this, some governments have enacted measures aimed at providing a more significant female presence in legislative bodies, generally determining that the parties include a certain proportion of women on their lists of candidates (Barrett et al., 2014).
In countries that do not have such devices, the mobilization of women by the adoption of measures in this direction is increased, while several parties have recognized that their lists are not adequately representative without a certain proportion of female candidates, even if the law does not require it. Similar discussions about the specific representation of racial or ethnic minorities are underway in the United States. Electoral district proposals or adjusted voting processes are debated to increase the likelihood of election of Hispanic candidates and maintain democratic stability in the country.
References
The United States Census Bureau. Texas Demographics Retrieved from https://www.census.gov/quickfacts/fact/table/tx/RHI725217#viewtop
Ranciere, J. (2006). Democracy, republic, representation. Constellations, 13(3), 297-307.
Duflo, E. (2005). Why political reservations? Journal of the Eu...
Cite this page
The Reasons for the Shifting Populations Into Texas Paper Example. (2022, Aug 23). Retrieved from https://proessays.net/essays/the-reasons-for-the-shifting-populations-into-texas-paper-example
If you are the original author of this essay and no longer wish to have it published on the ProEssays website, please click below to request its removal:
- Paper Example on Class Differences in Howards End
- Essay Sample on Gender Roles
- A Critical Analysis of George Sodini and Social Control Theory Paper Example
- Essay Example on Global Communication: Exploring Cross-Border Connections
- Essay Example on Native Americans in Z Nation: Misrepresentation and Stereotypes
- Critical Essay: Eva Derzic's Perspective on Communication
- Essay Example on US Immigration: An Economic and Social Analysis